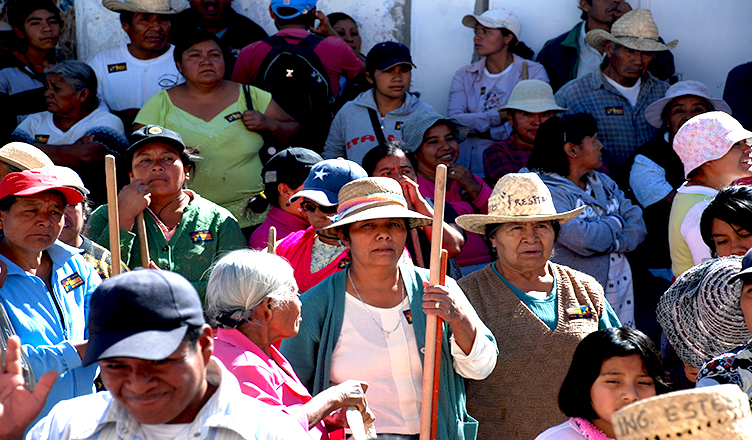
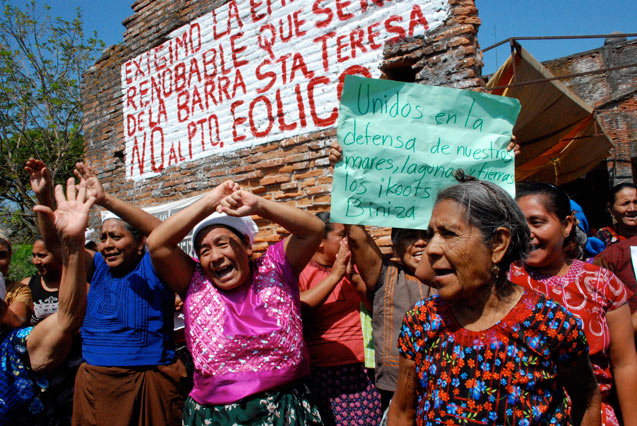
The Afro-Brazilian Quilombola people were forced from their land in Brazil in order to make way for eucalyptus plantations, which produce toilet paper destined for Western markets. But they are resisting by replanting native trees and food crops, and working for a post-eucalyptus reality.
The principal use for the cellulose found in eucalyptus plants in Brazil is disposable paper products, such as toilet paper and paper towels - products most in demand in first-world markets. Yet these types of paper products generate social and environmental impacts in places in Brazil where many communities have never even had access to them.
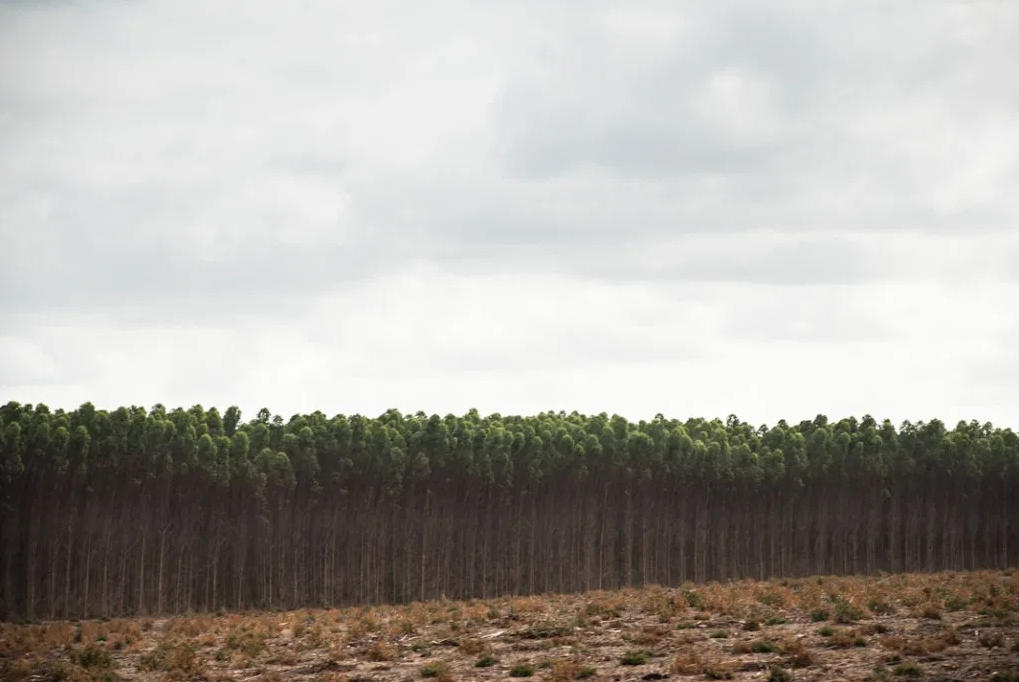
The region known as Sape do Norte, which includes the cities of Sao Mateus and Conceicao da Barra, in the state of Espirito Santo, in Brazil, has been heavily affected by eucalyptus plantations. In Sao Mateus, for example, the plantations occupy 70 percent of the territory. From Vitoria, the capital of Espirito Santo, to Sao Mateus, a stretch of close to 300 kilometers in length is covered by eucalyptus trees. In some places, small remnants of the native forest and its biodiversity can be seen, but only for a few hectares, quickly passed by in a car.
"There were monoculture plantations in unlikely places, near springs and in zones where aquifers are replenished. The forests along the riverbank were cut down; the path of the water was cut off; lakes were filled in with dirt - and the biodiversity of the Atlantic forests was decimated with insecticides and herbicides."
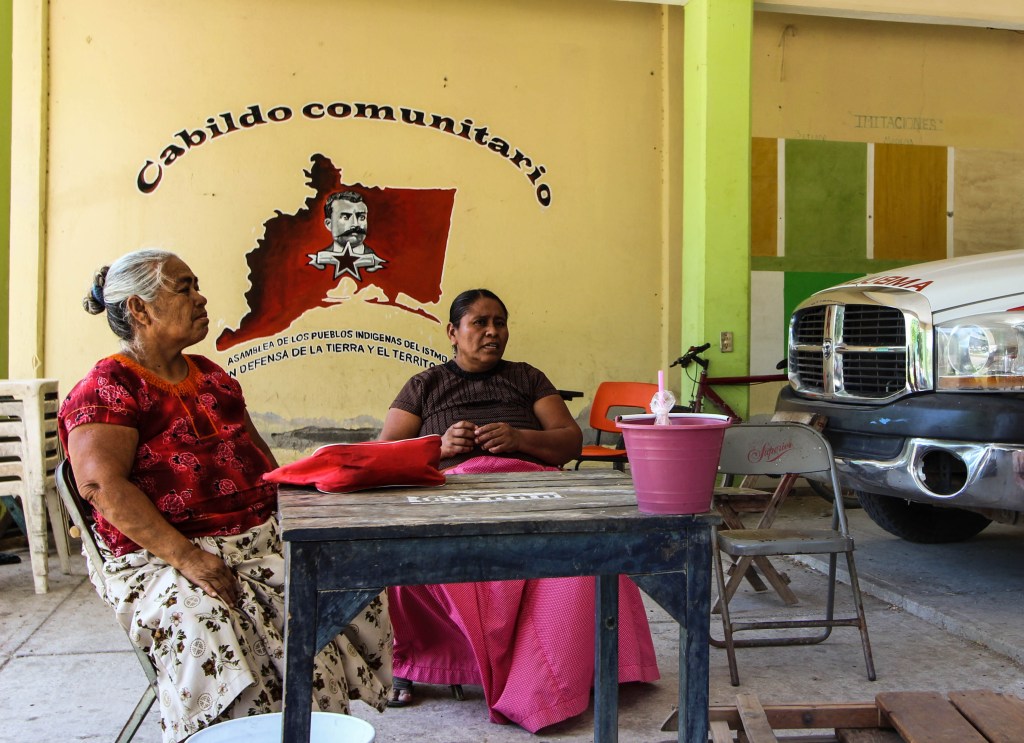
This area is also a symbol of Afro-Brazilian resistance; it is the land of the Quilombolas. The name Quilombola comes from the Kimbundu language, one of the Bantu languages widely spoken in Angola. Places where rebel or fugitive slaves lived were called quilombo - in hidden corners of the city or out in the countryside. From there the word Quilombola is derived, used in Brazil to describe a rebellious person of African descent.
"Quilombola is a specific type of person of African descent. They were brought from Africa during colonial times like the others, but they refused to submit to slavery and represented Black resistance. They built communities, called quilombos, fleeing from slavery in Brazil, living in isolated communities made up of 20 or 30 families, where they lived autonomously. Their descendants stayed in those in these places," Marcelo Calazans told Truthout. He works with the Federation of Organizations for Social and Educational Assistance (FASE), an organization that has worked for 30 years on issues related to the impacts of eucalyptus cultivation in the state of Espirito Santo.
In Sao Mateus, there was a port where people recently brought from Africa were bought and sold. Many of them fled the ships before they reached the docks. They escaped and sought refuge in the forests.
Slaves were emancipated in 1888, but emancipation was not accompanied by measures that would have permitted Afro-Brazilian communities to continue living in rural zones. A century later, these communities were legally recognized in the 1988 constitution, although it did not guarantee the preservation of the quilombo territories. With or without official recognition, a large number of these communities survived in rural areas, as evidenced by the communities of Sape do Norte.
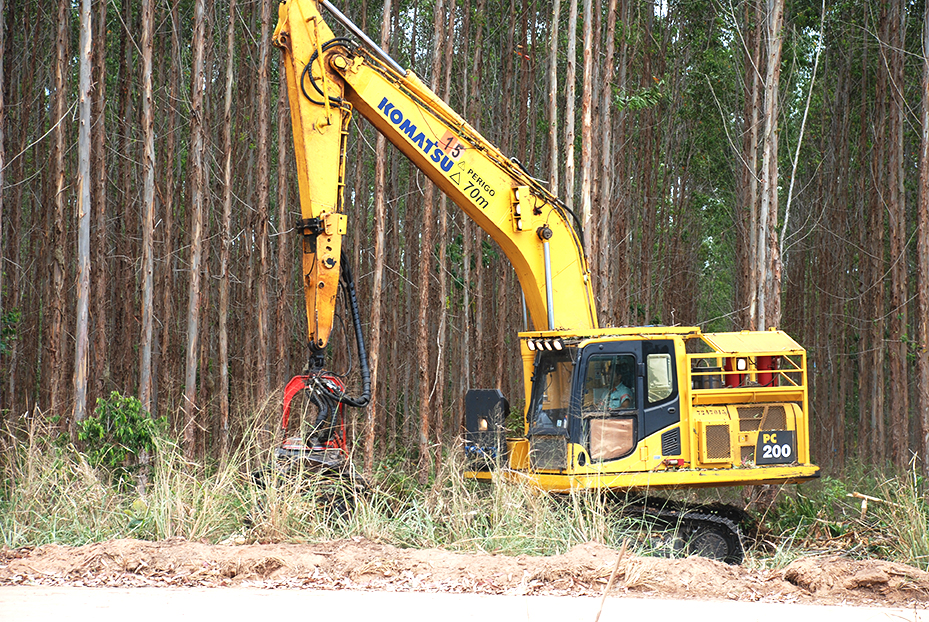

The machine that cuts down the eucalyptus trees. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F)
It is a forest without flowers, without smells, without animals; not a single bird flies through this place.
In the 1960s, with the arrival of the eucalyptus cellulose extraction industry, the Quilombolas suffered a new blow and families were forced to abandon their land, some moving to the big cities in search of survival, where they ended up in the huge favelas, or slums. It is estimated that before the arrival of eucalyptus, there were around 15,000 Quilombola families. Today that number has dropped to 1,200 families who reorganized themselves into 32 communities in Sape do Norte. These Quilombola descendants are dispersed in communities isolated from one another by eucalyptus plantations, living under the pressure of the cellulose industry and its effects.
"There were monoculture plantations in unlikely places, near springs and in zones where aquifers are replenished. The forests along the riverbank were cut down; the path of the water was cut off; lakes were filled in with dirt - and the biodiversity of the Atlantic forests was decimated with insecticides and herbicides. This in turn made agricultural cultivation impossible, unless pesticides were used," according to Simone Batista Ferreira, a researcher with the geography department of the Federal University of Espirito Santo.
A Global Leader in Cellulose Extraction
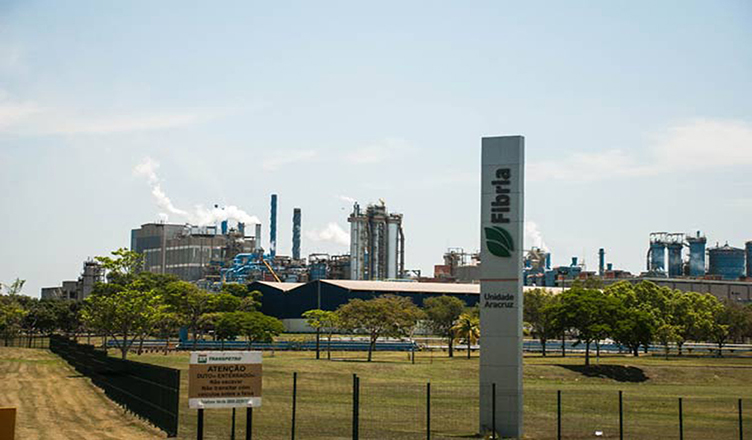
The company Aracruz Celulose arrived in Espirito Santo in the 1960s. It was initially made up of shareholders such as Souza Cruz (a subsidiary of British American Tobacco), the Lorentzen family Group - which is connected to Norwegian royalty - and the Safra Group, with each having 28 percent ownership. The Brazilian state was a partner through its purchase of stock through the National Economic Development Bank (BNDE) - now referred to as the BNDES - for a share later reduced to 12 percent. In 2009, Aracruz Celulose changed its name and Fibria Celulose was born, the result of the merger of Aracruz Celulose and Votorantim Celulose and Paper (VCP). Today, Fibria is considered a global leader in the production of eucalyptus cellulose. It is the only company in the global forestry industry that is listed on the Dow Jones index and traded on the New York Stock Exchange.
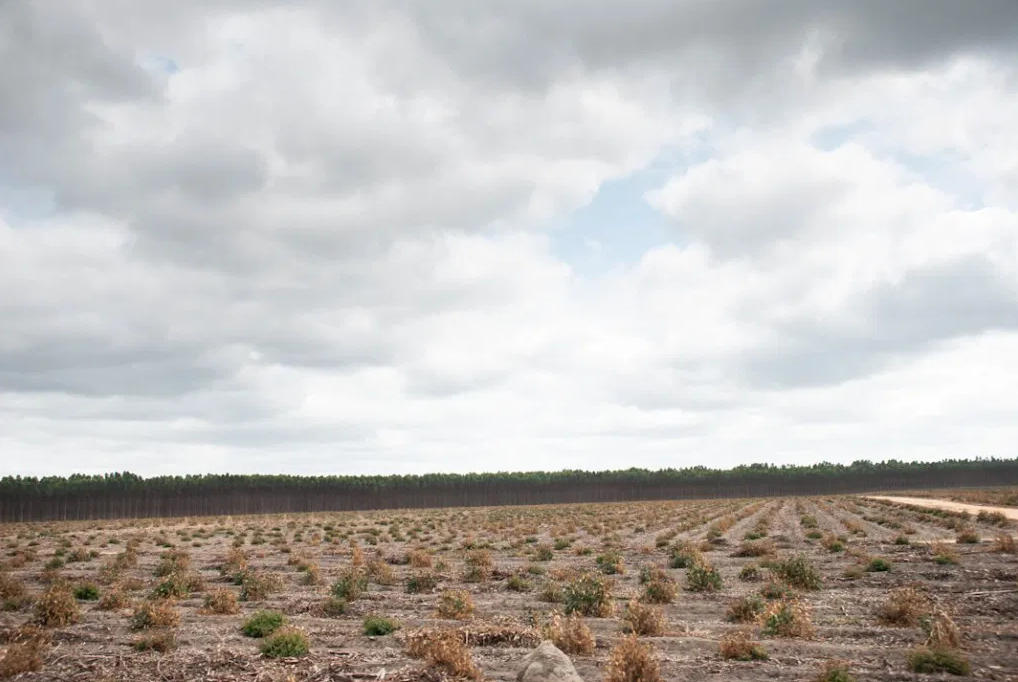

Lifeless Forests
It is a forest without flowers, without smells, without animals; not a single bird flies through this place - a dubious forest, of a uniform green color, full of emaciated trees with thin, tall trunks that look like shaky pillars. In Ecuador, eucalyptus plantations are known as silent forests because there are no birds. In Chile, they are called military forests because, aside from their green characteristic military-uniform hue, the trees are planted in rigid lines. In Brazil, they are called "green deserts" because they contain no life.
Brazil is the fourth largest producer of cellulose worldwide, after Canada, the United States and China. According to the 2014 report on the Brazilian Tree and Forest Industry (IBA), with statistics from 2013, the area where forests were cultivated in Brazil reached 7.6 million hectares in 2013. Eucalyptus represents 72 percent of the total, with a total area of just under 5.5 million hectares. In 2013, 15.1 million tons of cellulose and 10.4 million tons of paper were produced. The industry's objective is to reach production levels of 22 million tons of cellulose in Brazil by the year 2020.
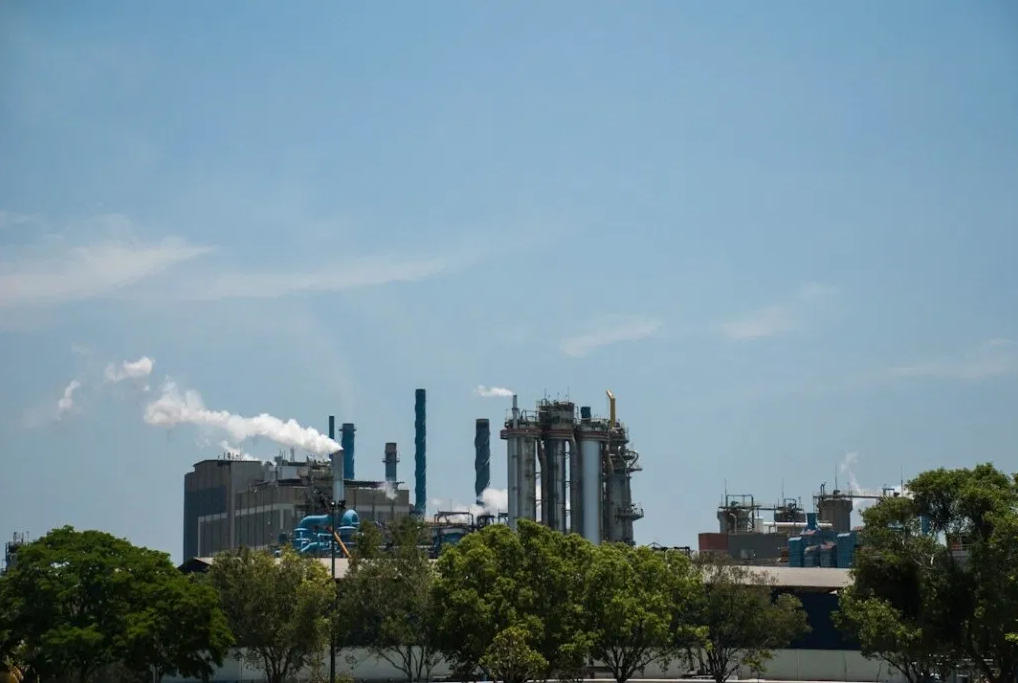

Paper factory in the city of Aracruz. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F)
International Demand
According to economist Helder Gomes, a member of the Alert Against the Green Desert Network, in the 1960s, international markets were under pressure due to increased demand for pulp and paper and the difficulty of widening production in countries where eucalyptus had traditionally been produced. "In the 1960s, studies done by the FAO [UN Food and Agriculture Organization] indicated the difficulty of expanding production in producing countries, due to the availability of land in central countries, the long period of maturation and the pressure from social movements against the rise in contaminating emissions and against the expansion of monocultures," Gomes told Truthout.
This forced international bodies, such as the FAO itself, Gomes said, to begin subsidizing the expansion of forestry programs in countries like Brazil, where there were favorable ecological conditions for the rapid growth of forests, available land, an abundance of cheap labor, and government policies that would benefit and support the industry.
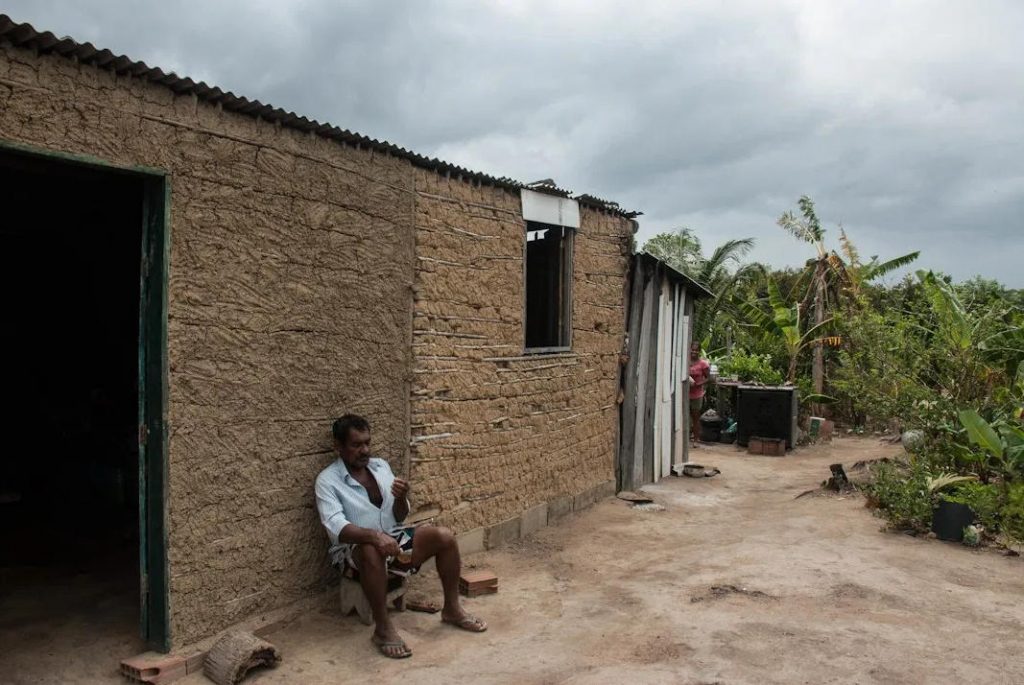

A quilombola house in a reclaimed area. There were eucalpytus plantations here for over 49 years. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F)
Destruction
Aracruz Celulose is directly responsible for the destruction of at least 43,000 hectares of tropical rainforest in the municipality of Aracruz. It is a municipality that, in addition to the plantations, is home to three of the primary factories that process tree cellulose.
"Of the 40 indigenous communities that existed during the first years of this industry, only six remained."
This destruction was documented in an environmental impact evaluation report completed by the Technological Institute of the Espirito Santo State University in 1988, which was required in order for the company to obtain the permits for its first production expansion. According to the report, "through aerial photograph analysis obtained at the start of the 1970s, it was found that 30 percent of the surface of Aracruz was covered by native forests, which were then substituted for homogeneous eucalyptus trees."
Aracruz did not only destroy the forest, but also forced the communities that lived there to leave. "Of the 40 indigenous communities that existed during the first years of this industry, only six remained," said Sebastiao Ribeiro Filho, a lawyer and member of the Alert Against the Green Desert Network.
Toxic Bleach
The chain of production of cellulose, beyond creating homogeneous landscapes, also produces noxious smells. While walking through the city of Aracruz, the air is suddenly filled with an acidic stench. "It's bleach!" said FASE's Calazans, who tells us why it smells like it does. "In order to bleach the paper, millions of liters of chemicals are required, among them hydrogen peroxide and bleach, which are prohibited in many countries. There is no strict regulation of their use. Afterward, the waste goes directly to the sea."
"The World Trade Organization, the World Bank and governments that promote this system, which only a few multinational corporations benefit from, are causing an economic genocide and destroying traditional agriculture, and this means the destruction of entire towns and communities."
According to Luiz Alberto Loureiro, a former employee of Aracruz Celulose, the plantations are constantly attacked by pests and other plant species that have to be combated using chemicals such as Glifosato or Mirex. The insecticide is prohibited in all its formulations and uses because it is harmful to human health and to the environment. "The workers die of poisoning and from accidents, and they don't talk about this," Loureiro said. "Employees don't receive training regarding [the risk of] poisoning and many times they bring their work clothes home and wash them with their children's clothes."
Employment Promises
According to Sebastiao Pinheiro, agronomist and professor at the Rio Grande do Sul University, eucalyptus plantations do not generate employment; they actually destroy the source of employment for thousands of families. "The green deserts do not create jobs. Four hundred hectares of eucalyptus would be required to create one job. In family or small-scale agriculture, 10 people are required for one hectare. The World Trade Organization, the World Bank and governments that promote this system, which only a few multinational corporations benefit from, are causing an economic genocide and destroying traditional agriculture, and this means the destruction of entire towns and communities," Pinheiro told Truthout.

Fibria Celulose company. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F)
Memory of Destruction
"I remember the Atlantic forests. We lived off of agriculture in the countryside, and from hunting. I also remember when the company arrived. The devastation was not tree by tree; it was done using giant chains 100 meters long pulled by tractors, destroying everything in its path. Each link in the chain must have weighed 100 kilograms. There were trees with huge diameters that couldn't withstand the chains," John Ramos de Souza said. He is Quilombola and from the Angelim 1 community. "I saw many monstrous things done by the company. I saw without understanding, without knowing what the consequences would be, and now we are paying the price."
The National Public Ministry, in November 2014, suspended one of the credit lines of Fibria as a cautionary measure. It was the one from the federal government's National Economic and Social Development Bank that went to the Quilombola zone in northern Espirito Santo.
Fibria is being accused of fraud for the way it obtained land for its plantations. According to the lawsuit, at the beginning of 1970, former employees of the company claimed to be small-scale farmers before the state government in Espirito Santo, with the goal of obtaining titles for the "unused" land. Afterward, the employees transferred these property titles for land located between Conceicao da Barra and Sao Mateus, to Fibria. In the majority of cases, the period in which the areas remained legal property of the employees didn't last even a week before they were transferred.

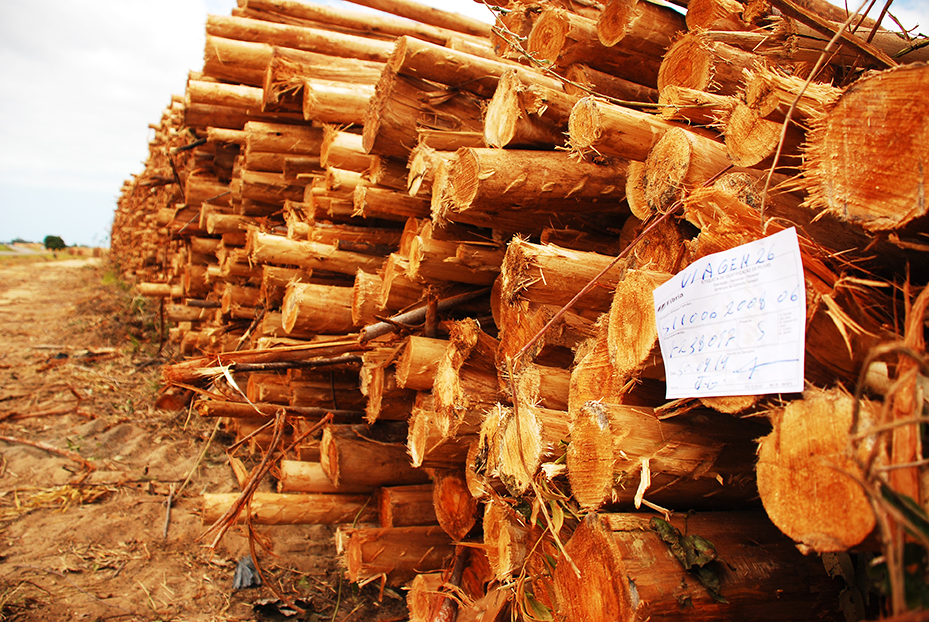
Eucalyptus trees harvested in one day. (Photo: Santiago Navarro F)
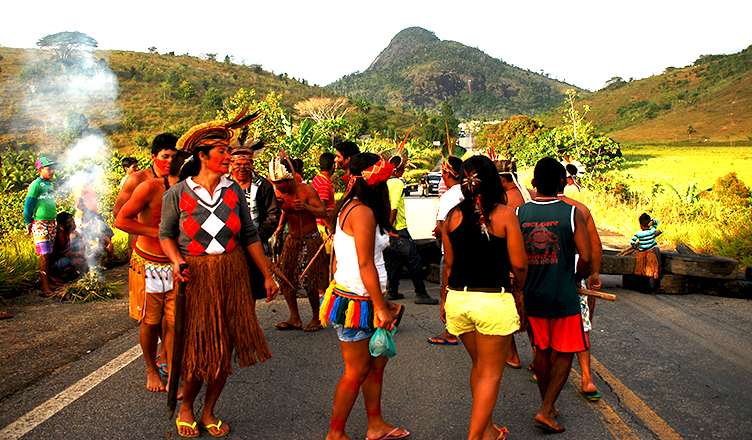
Quilombolas Resist Eucalyptus
ARUE Ticumbi. ARUE Ticumbi.
What did the people do wrong?
What did the people do that was so wrong?
These questions are part of a song that was sung by African descendants during the time of slavery and that the Quilombolas of Barra da Conceicao maintain as a tradition in a ritual called Ticumbi. In the song, they ask Saint Benito the causes of all the loss they have suffered: the loss of their land, the forests and the water resources.
Today, the song seems to gain another dimension in Ticumbi master Souza's voice: one of resistance. The culture of his ancestors serves as a point of strength in order to resist new forms of slavery, this time due to the neocolonialism of eucalyptus. "We are communities cut off by eucalyptus and we are here resisting," Souza said.
He tells the story of his father, who, in the 1960s and '70s was forced off his land twice, which is where he obtained subsistence for his family. "The people who claimed to be the owners of the land showed up and pressured us to leave. At that time we were afraid and we left. It was more difficult to confront. And that was how the land was transferred to the company [Aracruz]," he said.
"We have no time to lose. Our path against eucalyptus means returning to the land that belonged to our ancestors and continuing to grow food."
Resistance is no longer sufficient, according to Vando Falcao Souza, John Ramos da Souza's son. Advancing is crucial. "We have no time to lose. Our path against eucalyptus means returning to the land that belonged to our ancestors and continuing to grow food," he tells Truthout.
Angelim 1 is a place of land recovery for the Quilombola families. After the clear-cutting of trees by the company, families returned to the area and began a process of soil regeneration. "After 40 years of planting eucalyptus in the same place, a transition process is necessary. The soil is very dry; it rains and the water disappears. Many said that we wouldn't be able to plant anything, but we are seeing that with patience and a lot of work it is possible. In five years I think we will be able to make it so that the soil is how it was before the eucalyptus were planted," said Falcao.
New plants have already started to flower, and they call them the transition to a post-eucalyptus time. Generally, the transition is started with plants such as watermelon, yucca, pumpkin and beans. "Corn and coffee still won't grow. We are already growing various species of beans and we are starting to sell them in small markets in the community. The goal is to form a sort of cooperative here," he said.
Leaving the Senzalas
A few kilometers from Angelim 1, land recuperation is also taking place in Linharinho. There, the transition effort is to plant according to an agroecological model in order to recuperate the soil, which means planting food crops along with native forest species. "After clearing the land of eucalyptus, the technique is to plant trees from a native forest that are brought from other places, and around these trees, other crops such beans and pumpkins are planted. This is how we are going to rebuild the forest and the harvest at the same time. The process is slow, it will require even six or seven years for the wild animals to return again and for the water resources to recover," Antonio Rodrigues de Oliveira, who is Quilombola, told Truthout.
"What we are doing here is what our ancestors did. They fled from conditions of slavery and created conditions for life in isolated places. They opened clearings and produced from the earth."
Rodrigues says that he arrived in this place with few resources, with only his head held high, his hands, and the necessary courage. "We can't expect anything from the government, or from the corporations, or from anyone. We have to take up the hoe, go into the land, build a hut, dig a well . . . carry water, even push with a donkey if necessary. Never again will we die of hunger . . . no, no, we will not die. We will go slowly because we don't have infrastructure, but we will do it," he said.
He also says that the situation is difficult and he remembers that the company arrived to plant eucalyptus even in the cemetery where his grandparents were buried. "They left us with almost nothing, just some adapted rodents, wild pigs and armadillos living as we lived, migrating and searching for what was necessary to survive." He believes, however, that there is no time to complain; it is time to work hard and rebuild what has been destroyed.
He doesn't hesitate to compare the situation in his community to that of his ancestors. "What we are doing here is what our ancestors did. They fled from conditions of slavery, known as Senzala [the place where slaves were held as prisoners on huge plantations] and created conditions for life in isolated places. They opened clearings and produced from the earth. Here is a Quilombo, the place of liberation," said Rodrigues, who has worked on various plantations and at one point migrated to the city.
Culture of Transition
Within the cellulose industry complex, the number of eucalyptus trees that are harvested every day establishes the rhythm and velocity of production. In order to operate at maximum production levels, a culture of homogenization must prevail. Flat land, long trees that are thin and without branches, and soil free of impediments are key. Here, diversity is an obstacle.
"Perhaps in 100 years, a Quilombola individual will look at the eucalyptus plantation and say that it is a forest, because he won't have the reference of what a native forest is. The cellulose company knows that if this memory is broken, there will be no more problems with resistance."
Joao Guimaraes, also from Angelim 1, tells Truthout that it is necessary to build the knowledge that will allow a cultural shift in the transition to a post-eucalyptus reality. "We can no longer live lamenting the disappearance of the river and the fresh water spring that dried up and the trees that disappeared, the birds that have left. The Atlantic Forest is gone now, and we have to regenerate it. These 40 years of eucalyptus plantations will not be forgotten overnight, which is why we have to work hard, experimenting with how it is that we are going to go about this recovery, with trial and error, in order to build transitional knowledge," Guimaraes said.
The land that has been retaken is part of this process. "These areas are serving so that we can create this understanding of the transition. We live with certain amounts of tension due to the fact that this land is being disputed and they could force us to leave at whatever time the company requests it. But we have no other option. As they advance with their modern machines, our form of insurgence is to plant food with our hoes. It's slow, but we are recuperating the land and our independence," he said.
This is the first generation that is retaking land primarily for the production of food. "It is the memory of the oldest ones that is strengthening our struggle," Guimaraes told Truthout.
The Struggle for Memory
One of the controversies at play is the memory of what the Atlantic Forest used to be and the passing on of this memory to the younger generations. "Perhaps in 100 years, a Quilombola individual will look at the eucalyptus plantation and say that it is a forest, because he won't have the reference of what a native forest is," Calazans said. "The cellulose company knows that if this memory is broken, there will be no more problems with resistance."
The generation of people in the state of Espirito Santo that remember the Atlantic Forest will be gone within the next 30 years. "These people have seen and lived in the forest. If they die and we still have not transitioned beyond eucalyptus back to native forests and traditional agriculture," said Calazans, "it will never happen."
"Memory assures the dream of these territories. The day that memory dies completely, we will no longer be able to think in a post-eucalyptus time," he added. "We have to invest in building understanding of this transition. These next three decades are strategically important in this fight."
Published in Truthout